Definition of Limits- If f(x) becomes arbitrarily close to a unique number L as x approaches c from either side, the limit of f(x) as x approaches c is L.

*Note- the limit doesn't care what is actually happening at c
Example-
Example-
Even though this graph has a hole at x=1, the graph still approaches 2 from both sides so the limit is still 2. The limit doesn't care what is actually happening at f(1).
Example-

.gif)
.gif)

.gif)
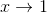.gif)

.gif)
.gif)


No comments:
Post a Comment